Boosting Website Performance with CSS Optimization
In web development, the developer thinks the only thing to worry about is Javascript but CSS also plays a vital role and can be the reason for the chunky user experiences. Having a good fundamental knowledge of CSS can make your app more engaging and smooth.

Introduction
There are a lot of ways like SVG, Javascript, canvas, WebGL, CSS animation, etc. to achieve animation on the web. In comparison to Javascript, animating elements using CSS can be easier. CSS animation can also give better performance, as it gives the browser more control while rendering frames, and to drop frames if necessary.
However, the web performance depends on the CSS properties that we are using for the animation. Expensive CSS properties can result in jank. To understand all these things let take a deep dive into:-
- How CSS works?
- How CSS can effect web performance?
- How we can optimise web performance?
How CSS works?
To understand the CSS functionality and how it may effect UX first, we need to understand how CSS works.
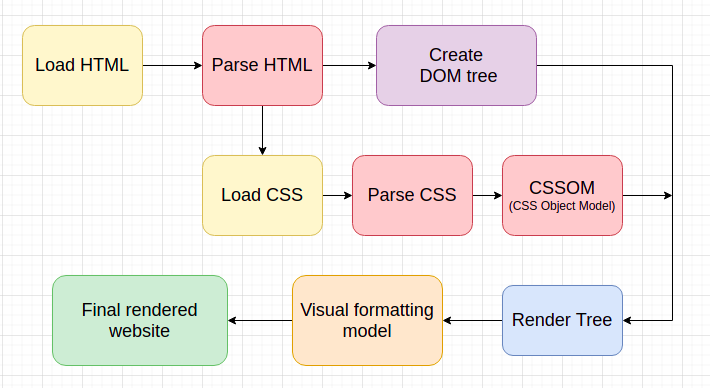
When a browser displays a document, it must combine document content with its style. Browser used to follow the following stages while this whole process.
-
The browser makes a get request to the server and the server and gets the HTML file in the response.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <main> <h1>Hi</h1> </main> </body> </html> -
As soon as browser get the HTML it starts parsing it and gives us nodes like
<head>,<body>, etc. and these node makes theDocument Object Model (DOM). The DOM of the above HTML snippet will look like this.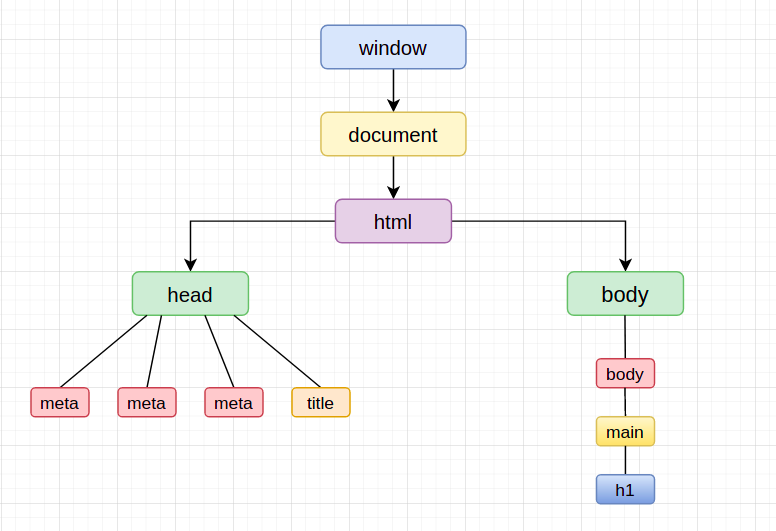
-
The browser then fetches the resources that are linked to the HTML document such as CSS, Javascript. CSS basically comes from
UserAgents,stylesheet,inline-css, etc. -
As soon as the browser fetched the CSS it starts parsing the CSS and calculate which rules should be applied to which node in DOM, and add style to those nodes. This process is known as
Recalculate Stylesin Dev Tools.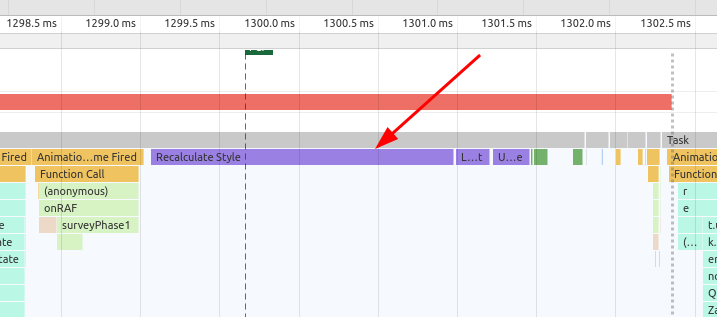
-
When the browser is done with the
Recalculate Stylesprocess we used to get a new tree i.e.Render Tree. Render tree looks like the DOM but without any<head>,<scripts>, etc. -
Once the browser knows which rules to apply to an element, it can begin to calculate
Layout. In Layouting, CSS calculates how much space an element will take and where it will align on the screen. In dev tools, this process is known asLayout.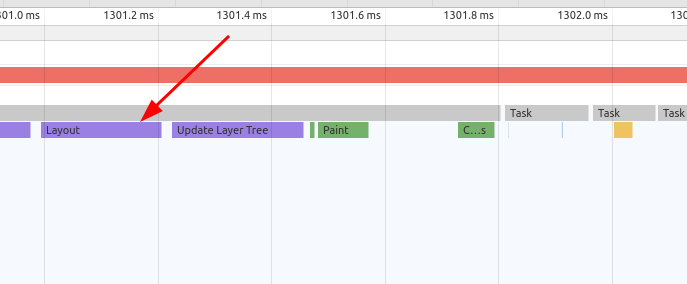
-
When the browser finishes
Layoutwe will get the properly aligned element in theVectorform. Vectors are just shapes. Now browser needs to covert it toRasterform. To covert, a vector shape to the raster browser needs to fill every pixel of the element. Conversion of vector to raster is taken place with the help ofRasterizerand this process in the dev tools known asPaint.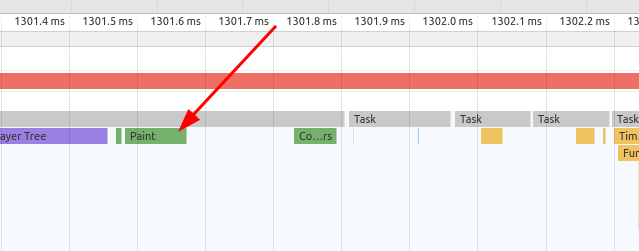
After all these steps the browser will render the element on the screen. So, these are basic working of CSS and steps that make a frame.
How CSS can effect the web performance?
In the UX world, animation plays a vital role and users expect all the interaction to be smooth. Animation can help us to make our website much more interactive and engaging but if it will not be handled properly then it can make our website slower and janky.
Responsive user interfaces are used to follow a frame rate of 60 frames per second (fps). It is not always possible to maintain 60fps but to make a better user interface it is mandatory to maintain a high and steady frame rate for all the animations. For 60fps the browser has 16.7ms to execute the CSS steps that we mentioned in the above section. So, if we execute the expensive CSS properties then there are higher chances that the browser might lose some frames and result in a jank.
In the modern computer that higher speed these janks might not be noticeable but with the CPU with the slower speed, it can be noticed easily. Let me show an example.
transition: margin-left 300ms ease-in-out;
In this example, expensive CSS properties have been used for the animation i.e. margin-left and we reduced the CPU speed by 6 times. Hence browser does not show frames with the rate of 60fps and it is dropping the frames that result in jank .
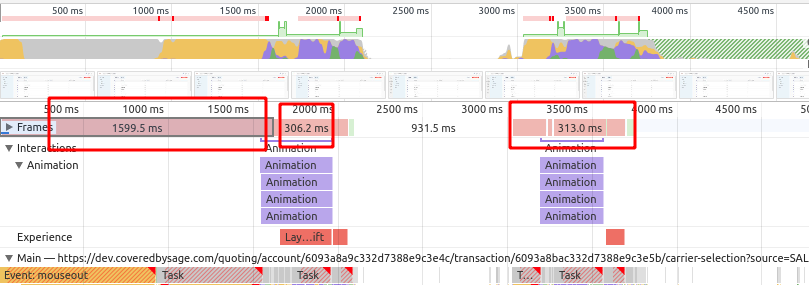
Let's understand why this is happening and how we can optimise it.
How we can optimise web performance?
To optimise the web performance let's do a quick recap. If we make visual changes then to render it on-screen browser mainly performs Recalculate styles , Layout , Paint , Composite Layers, and if the CPU speed is slow then to perform all these processes in just 16.7ms is difficult and browser might drop some frames. So, to optimise we can try to skip some big operations by using the best CSS property. Let's understand how we can skip some operations.
-
If we make some visual changes that can effect/change an element's geometry like its
width,height, orpositionwith relation to another element liketop,left. Then the browser will have to check all the other elements andre-flowthe page then effected areas will bepaintagain and painted elements will need to becompositedback together. In this case, browser is performing all the operations again, this is known asre-flow.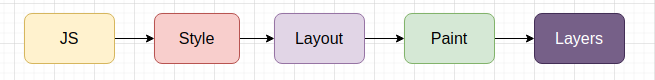
re-flowcan happen due to some CSS properties that causes layout shift likemargin,width,height, etc. -
Now, if we make some visual change that will effect/change an element's visual change only means that it only triggers
Paint. In this case,re-flowwill not happen and we can optimise our page.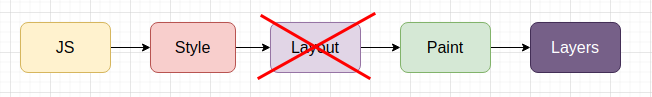
Some paint only CSS properties are
background-color,shadow, etc. -
If we use a CSS property that neither effect
Layoutnor effectPaintliketransform. Then we can skip two big browser operations and we browser will only take care ofComposite Layeroperation.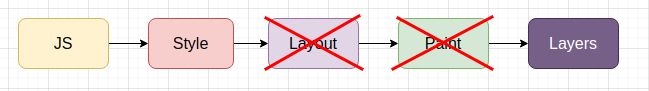
Now, it's time to use the knowledge that we have gain and optimise our example that we used above. In the example, we are using margin-left property in the animation and we discussed margin is a CSS property that can cause re-flow .
aside {
background-color: rgb(242, 242, 242);
box-shadow: rgb(0 0 0 / 5%) 0px 3px 10px;
width: 8.2rem;
display: flex;
-webkit-box-align: center;
align-items: center;
-webkit-box-pack: justify;
justify-content: space-between;
flex-direction: column;
min-height: 100vh;
z-index: 1;
margin-left: -8.2rem;
position: fixed;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
transition: margin-left 300ms ease-in-out 0s;
}
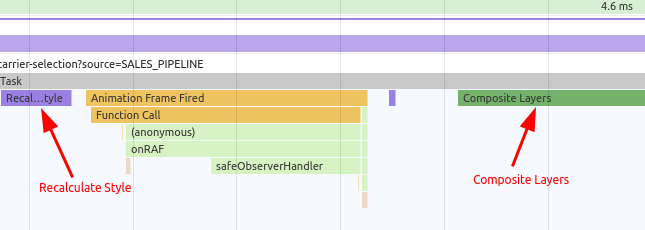
Hence re-flow :
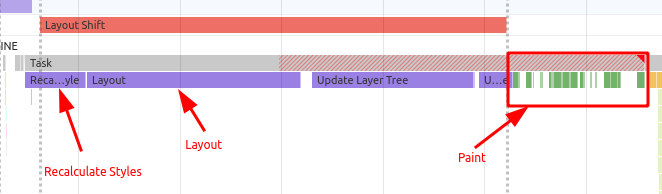
In this performance review, we can see the browser is doing Layout , Paint operations. Now browser has to perform all the operations in 16.7ms and it might be very difficult to finish all the operations in 16.7ms hence browser will drop the frames.
Result:
Optimisation
To optimise this let's use transform property which has a value translate by which we can achieve the same animation that we are doing with the margin-left .
.css-1ysrssh {
background-color: rgb(242, 242, 242);
box-shadow: rgb(0 0 0 / 5%) 0px 3px 10px;
width: 8.2rem;
display: flex;
-webkit-box-align: center;
align-items: center;
-webkit-box-pack: justify;
justify-content: space-between;
flex-direction: column;
min-height: 100vh;
z-index: 1;
transform: translate(0px);
position: fixed;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
transition: transform 300ms ease-in-out 0s;
}
Hence No re-flow :
In this performance review, we can see there is no Layout , Paint operation happened. Now browser only has to perform two operations in 16.7ms and it will be a very easy task to perform. Hence we have optimise our web page.
Result:
So, this is how we can optimise our web performance !!
To see which CSS property triggers which operations we can refer to this site.
So, these are the basic fundamentals by which we can optimise our web performance. There are a lot of other methods too. I will be writing more about this, till then happy coding, and don't forget to check the performance of your project !!
